Author: GEN
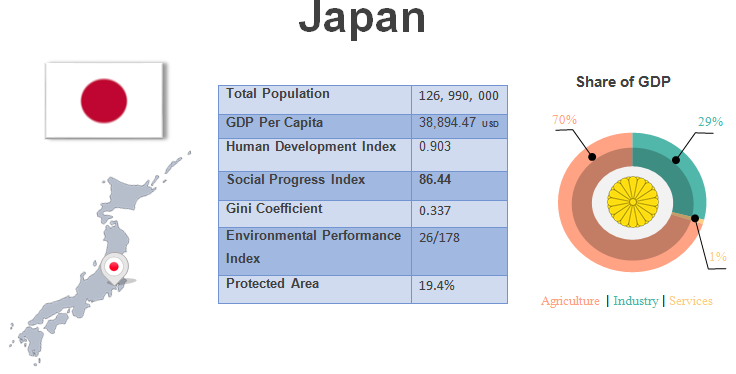
CSR in Japan
History of CSR in Japan:
- For over 50 years the topic has been publicly debated, slowly developing as a concept
- CSR in Japan traces back to a resolution issued by the Japan Association of Corporate Executives in 1956, entitled “Awareness and Practice of the Social Responsibilities of Businessmen.”
- CSR developed through five phases as defined by Kawamura.
CSR in Bangladesh
History of CSR:
- There is no specific legislation in Bangladesh to assist the regulation of
- CSR is gradually being normalised in Bangladesh, with CSR projects moving from the peripheral management by external actors, to the mainstream management within local companies.
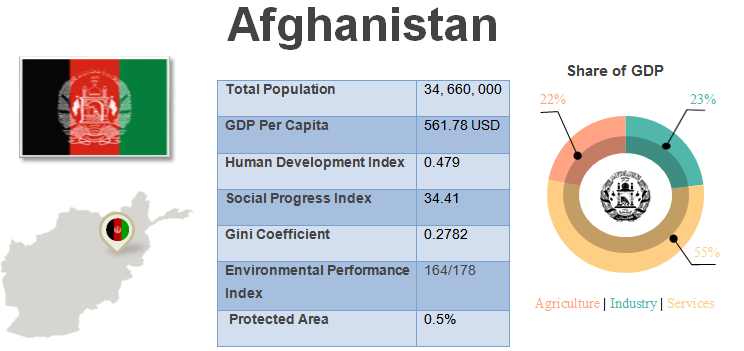
CSR in Afghanistan
History of CSR:
- Afghan awareness of responsible business conduct is nascent.
- A comprehensive mining law passed in October 2014 requires mining contract holders to consult affected communities.
- The largest Telecom operator in Afghanistan, Roshan, was recognized for its social responsibility in 2015.
About diamonds
- They arecomposed of carbon
- They burn when heated to bright red
- Their weight is measured in carat – 1 carat = 0.2 gram
- Diamonds were first discovered in India by Alexander the Great in 327 BC; then discovered in Brazil and described as “curious pebbles in 1725
The United States are the largest consumer of gem-quality diamonds in the world, but interestingly enough has no commercial mine production; the Crater of Diamonds State park in Arkansas is the only produce where the United States produces gem-quality diamonds.… Read More
Intro to Shared Value
Intro to Shared Value
Michael Porter, Harvard Business School Professor, and Mark Kramer wrote an article in 1999 called “Philanthropy’s New Agenda: Creating value, which discussed the idea that foundations could truly increase their social impact and adopt strategies aimed at creating value, instead of just pouring grant dollars.… Read More
The Rarest Diamond
It is estimated that there are only 30 red diamonds in the world, with each being less than half a carat. Its red color is due to an atomic deformity caused by extreme pressure.… Read More
State, Corporation and Tribal Community-Bauxite Mining in Odisha
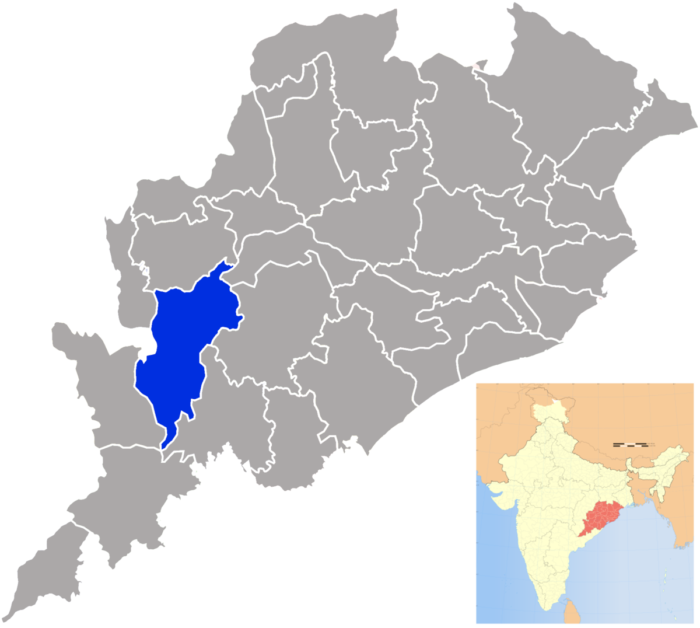
Odisha is one of the poorest states in India where half of the population operates below the national poverty line. In terms of Human Development Index, it ranks 22 among 29 Indian states (1).However, it is striking that it had recorded a stunning GDP growth of 8.74% (higher than India’s GDP 8.49%) in the period between 2004-2009.… Read More
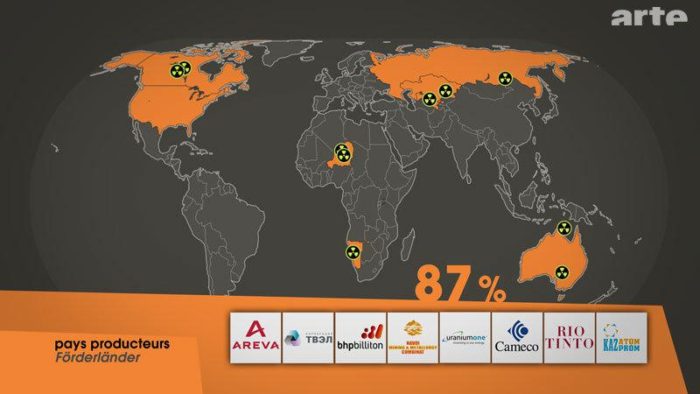
Resource Card : Uranium
Principal region of extraction : Canada, US, Russia, Australia, Kazakhstan, Niger, Namibia
Method of extraction : in 2012
- in-situ leach (44.9%)
- Underground mining (26.2%)
- Open pit (19.9%)
- Heap leaching (1.7%)
- Recovering from seawater (residual)
Stakeholders : Producing States, Multinationals (see map above), States using uranium to produce electricity (see map below), miners, local populations, some NGOs, supranational organs (UN, EU…)…
Key issues :
- Health risks of uranium mining : lung cancer
- Need for clean-up efforts
- Environmental effects : impact on surface water quality and quantity, groundwater quantity and quality, soils, air quality and biota
- Management of waste and its environmental consequences
- Industrial accidents (Chernobyl, Fukushima…)
- Distribution of income
Exchange rate : NYMEX : 24.40 USD (-2.40%)… Read More
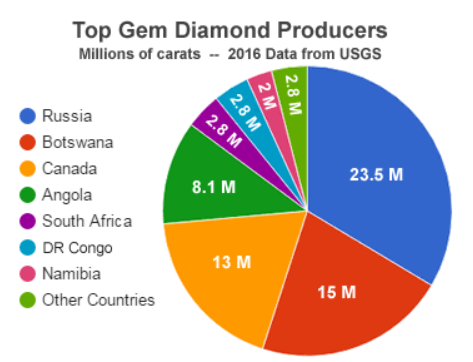
Resource Card : Diamond
Main regions of extraction : Botswana, Russia, Canada, Namibia, Angola, South Africa, Zimbabwe, Australia, Congo (in 2015)

Method of extraction : industrial or traditional
- Pipe mining (primary deposits): open-pit mining, underground mining
- Alluvial mining (secondary deposits)
- Marine mining
Process of recovery :
1- Crushing
2 – Scrubbing
3 – Cyclonic separation plant
4 – Recovery
5 – Cleaned, weighted and packaged
Stakeholders : States, mining firms, luxury goods industry, customers, rebel armed groups, workers…
Key issues :
- Conflict/blood diamond : human right abuses, labor conditions, child labor, violence, civil wars…
- Kimberley Process : ignores some issues (human rights abuse, environment…)
- Environmental costs : land and water devastated
- Illegal mining
- Traceability
Exchange rate : Mineral : Nasdaq OTC Bull : 0.0228 USD (+3.64%)
Other key words :
4 C’s : cut, clarity, color, carat weight
Synthetic diamonds
Ethical diamonds